Alzheimer’s disease has long been regarded as an irreversible condition. However, a new study conducted by American scientists reveals that an imbalance in brain energy supply is a key factor contributing to the deterioration of the disease. Animal experiments demonstrate that restoring energy balance via medication not only repairs damaged brain tissues, but also fully restores memory and cognitive functions in mice with advanced-stage Alzheimer’s disease, thereby reversing disease progression. This groundbreaking discovery opens up possibilities for a cure for Alzheimer’s disease. Relevant findings have been published in the latest issue of Cell Reports Medicine.

For more than a century, most research on Alzheimer’s disease has focused on preventing or slowing down disease progression, with very few attempts to reverse the damage already incurred. Despite massive research investment, no drug worldwide has set cognitive function recovery as a clinical trial endpoint to date.
To address this situation, a research team from Case Western Reserve University and Cleveland Clinic in the United States used mouse models and brain tissues from human patients, and found that the brains of patients struggle to maintain normal levels of NAD+, a critical cellular energy molecule. This deficiency directly drives the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
The team administered a drug named P7C3-A20 to restore NAD+ balance. The experimental results are encouraging: Restoring energy balance in the advanced stage of the disease repaired pathological lesions induced by gene mutations in the mouse brain. Both strains of model mice exhibited a full recovery of cognitive functions. Blood tests also showed that phosphorylated tau217, a key biomarker associated with Alzheimer’s disease, returned to normal levels. These robust pieces of evidence strongly demonstrate that the progression of Alzheimer’s disease can be reversed.
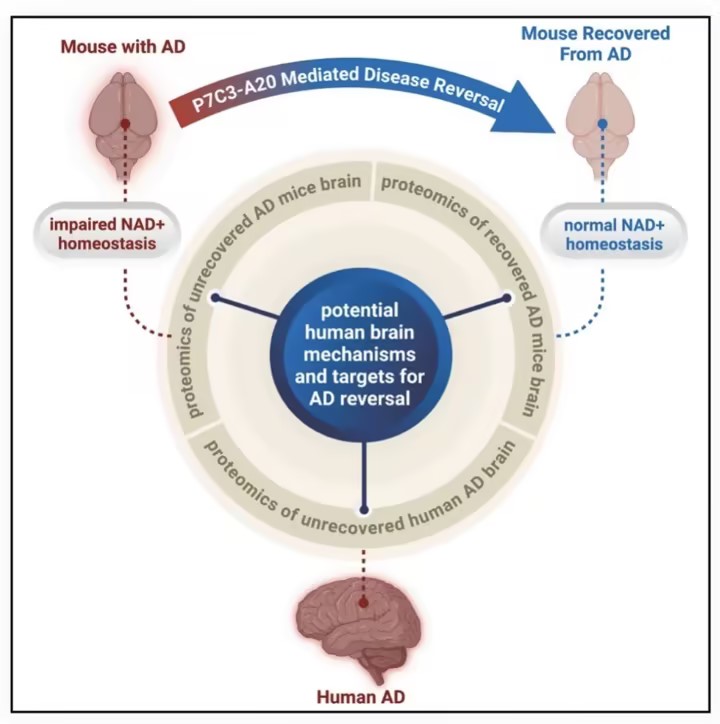
The research team emphasized that this therapy is distinct from the common NAD+ supplements available on the market. Such supplements may cause abnormally elevated NAD+ levels in the human body, which in turn increases cancer risks. In contrast, P7C3-A20 is a precision regulatory drug. It helps cells maintain NAD+ balance under stress and prevents uncontrolled fluctuations in NAD+ levels.
This discovery not only opens a new direction for Alzheimer’s disease treatment – shifting the focus from slowing down degeneration to restoring lost functions, but also lays a solid foundation for subsequent human trials.
For the next step, the team plans to further explore the key mechanisms underlying brain energy balance. This will verify whether the therapy is applicable to other age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Meanwhile, they will advance rigorous clinical trials to confirm its efficacy in human patients.
